© All rights reserved. Powered by Techronicler

AI-Powered Cybersecurity: The Next Frontier in Enterprise Defense
By Supratim Sircar, Software Engineer & Emerging Thought Leader

The cybersecurity landscape is undergoing a seismic transformation as artificial intelligence emerges as both the ultimate weapon and the primary battleground in the digital security arms race. With cybercrime costs projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, representing a 15% year-over-year growth, the integration of AI into cybersecurity has evolved from an innovative advantage to a critical survival imperative for organizations worldwide.
The Perfect Storm: Why AI Cybersecurity is Critical Now
The Evolution of Cyber Threats
The modern threat landscape has fundamentally changed, with cybercriminals increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence to create sophisticated, automated attacks that can adapt and evolve in real-time. The traditional reactive approach to cybersecurity, which relied heavily on signature-based detection and manual incident response, is no longer sufficient against these advanced persistent threats.
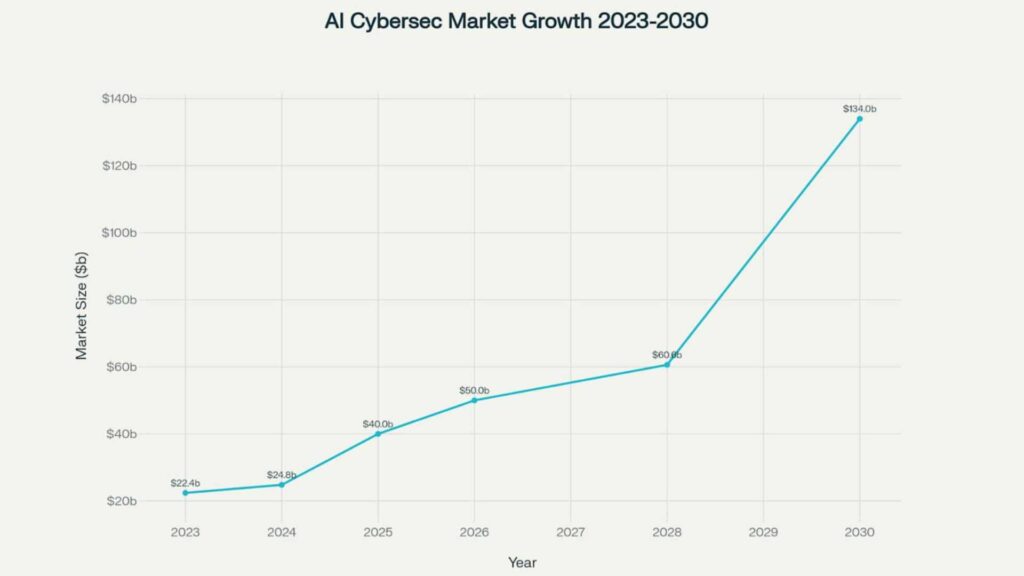
According to recent industry analysis, the global AI cybersecurity market is experiencing explosive growth, valued at $22.4 billion in 2023 and projected to reach $60.6 billion by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of 21.9%. This growth trajectory reflects the urgent need for intelligent, automated security solutions that can match the sophistication of modern cyber threats.
The Economics of AI-Driven Security
The economic imperative for AI-powered cybersecurity extends beyond mere technological advancement. Organizations implementing AI-driven security solutions report significant cost savings, with some studies indicating that extensive use of AI and automation can reduce data breach costs by an average of $2.22 million. This cost reduction stems from faster threat detection, automated incident response, and reduced reliance on expensive human expertise for routine security operations.
The financial services sector, in particular, has embraced AI cybersecurity solutions to combat the increasing sophistication of financial crime. AI is expected to generate up to $1 trillion annually in additional value for the global banking industry, with applications ranging from real-time fraud detection to automated compliance monitoring.
The AI Cybersecurity Technology Stack
Core Technologies and Applications
The AI cybersecurity ecosystem encompasses multiple technological domains, each serving specific security functions. The market distribution across these domains reveals the strategic priorities of modern organizations:
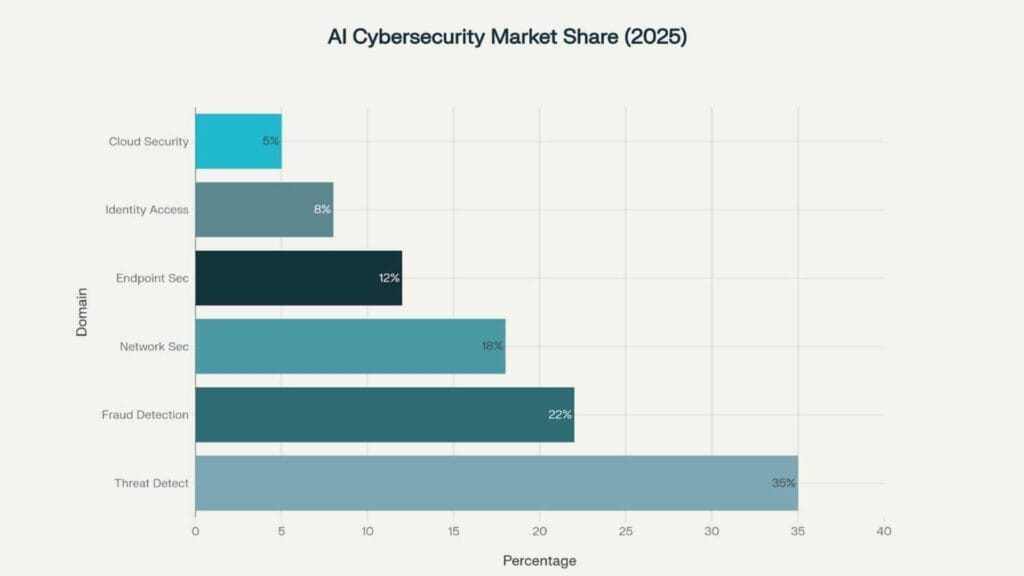
Threat Detection and Response (35% Market Share)
The largest segment of the AI cybersecurity market focuses on threat detection and response capabilities. These systems leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze network traffic patterns, user behavior, and system logs to identify potential security incidents. Advanced AI models can detect zero-day vulnerabilities and previously unknown attack vectors by identifying anomalous patterns that deviate from established baselines.
Modern threat detection platforms utilize various AI techniques including:
- Behavioral Analytics: Machine learning models that establish normal user and system behavior patterns, enabling detection of insider threats and compromised accounts
- Anomaly Detection: Advanced algorithms that identify unusual network traffic, system behavior, or data access patterns that may indicate a security breach
- Predictive Analytics: AI systems that forecast potential attack vectors based on historical data, threat intelligence, and environmental factors
Fraud Detection (22% Market Share)
AI-powered fraud detection systems represent the second-largest application domain, particularly crucial for financial institutions and e-commerce platforms. These systems process millions of transactions in real-time, applying sophisticated algorithms to identify potentially fraudulent activities without disrupting legitimate business operations.
The effectiveness of AI fraud detection systems stems from their ability to:
- Analyze multiple data points simultaneously, including transaction amount, location, time, and user behavior patterns
- Adapt to new fraud techniques through continuous learning and model updates
- Provide real-time decision-making capabilities that traditional rule-based systems cannot match
Network Security (18% Market Share)
AI-driven network security solutions protect the underlying infrastructure that supports all organizational operations. These systems monitor network traffic in real-time, identifying potential intrusions, malware propagation, and data exfiltration attempts.
Key capabilities include:
- Automated Network Segmentation: AI-driven systems that dynamically adjust network access controls based on user behavior and threat intelligence
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Advanced systems that use machine learning to identify and block malicious network activities
- Traffic Analysis: Deep packet inspection powered by AI algorithms to detect encrypted malware and sophisticated attack techniques
Emerging Technologies and Future Trends
Zero Trust Architecture with AI Enhancement
The integration of AI with Zero Trust security frameworks represents a significant evolution in cybersecurity strategy. AI enables continuous verification of users, devices, and applications, making real-time access decisions based on comprehensive risk assessments.
Key AI enhancements to Zero Trust include:
- Continuous Authentication: AI systems that continuously verify user identity based on behavioral patterns, device characteristics, and contextual information
- Dynamic Risk Assessment: Real-time evaluation of security posture based on multiple data sources and threat intelligence
- Automated Policy Enforcement: AI-driven systems that automatically adjust access controls based on changing threat conditions
Edge AI Security Solutions
The proliferation of IoT devices and edge computing has created new security challenges that traditional centralized security models cannot adequately address. Edge AI security solutions process data locally, reducing latency and improving response times while maintaining security at the network edge.
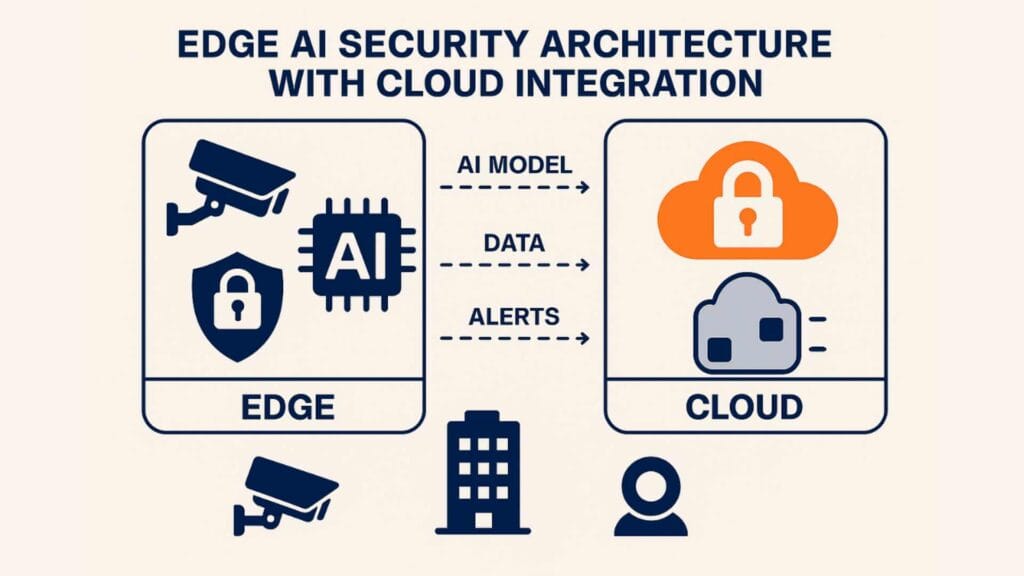
Edge AI security capabilities include:
- Distributed Threat Detection: AI models deployed at network edge points to detect and respond to threats locally
- Real-time Processing: Immediate analysis and response to security events without relying on cloud-based processing
- Bandwidth Optimization: Reduced network traffic through local processing of security data and events
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Financial Services: The Frontline of AI Cybersecurity
Financial institutions have emerged as early adopters and primary beneficiaries of AI-powered cybersecurity solutions. The sector faces unique challenges, including regulatory compliance requirements, high-value targets, and the need for real-time transaction processing.
Real-Time Fraud Detection
Modern financial institutions process millions of transactions daily, requiring sophisticated AI systems capable of real-time fraud detection without disrupting legitimate business operations. Companies like ACI Worldwide have developed AI-powered fraud management systems that combine machine learning algorithms with network intelligence to deliver precise fraud scores for financial transactions.
These systems analyze multiple data points simultaneously, including:
- Transaction patterns and history
- Geolocation and device information
- User behavior analytics
- Network intelligence and threat feeds
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance
AI-powered AML systems, such as those developed by C3.AI, help financial institutions detect suspicious activities while reducing false positives that burden compliance teams. These systems use advanced pattern recognition to identify complex money laundering schemes that may span multiple accounts, transactions, and time periods.
Cybersecurity Risk Management
The increasing adoption of AI in financial services also introduces new cybersecurity risks. As noted in recent regulatory guidance, AI implementations in financial institutions require robust governance frameworks to address:
- Model risk from flawed algorithms or biased data
- Cybersecurity threats including data breaches and adversarial attacks
- Operational risks from system failures or over-reliance on AI systems
Healthcare: Protecting Critical Infrastructure
The healthcare sector has become increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks, with the COVID-19 pandemic accelerating digital transformation and creating new attack vectors. AI-powered cybersecurity solutions are essential for protecting patient data, medical devices, and critical healthcare infrastructure.
Key applications include:
- Medical Device Security: AI systems that monitor and protect connected medical devices from cyber threats
- Patient Data Protection: Advanced encryption and access control systems powered by AI algorithms
- Ransomware Prevention: AI-driven backup and recovery systems that can detect and respond to ransomware attacks in real-time
Manufacturing and Industrial IoT
The convergence of operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) in manufacturing environments has created new security challenges. AI-powered security solutions provide comprehensive protection for industrial control systems, IoT devices, and manufacturing processes.
The global cyber security market for industrial automation is projected to grow from $12.96 billion in 2025 to $27.71 billion by 2031, representing a CAGR of 13.5%. This growth reflects the increasing recognition of cybersecurity as essential for maintaining operational continuity and protecting intellectual property in manufacturing environments.
Advanced Security Operations Centers (SOCs)
The Evolution of AI-Powered SOCs
Modern Security Operations Centers are undergoing a fundamental transformation driven by AI technologies. Traditional SOCs, which relied heavily on human analysts to monitor security events and respond to incidents, are being augmented with AI-powered systems that can process vast amounts of security data in real-time.

Automated Threat Intelligence
AI-powered SOCs leverage advanced threat intelligence platforms that automatically collect, analyze, and correlate threat data from multiple sources. These systems provide security analysts with real-time insights into emerging threats, attack patterns, and threat actor behavior.
Key capabilities include:
- Automated Threat Hunting: AI systems that proactively search for indicators of compromise and advanced persistent threats
- Incident Response Automation: Automated workflows that can respond to security incidents without human intervention
- Forensic Analysis: AI-powered tools that can analyze digital evidence and reconstruct attack timelines
Integration with Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR)
The integration of AI with SOAR platforms enables comprehensive security automation across the entire incident response lifecycle. Modern platforms like Torq HyperSOC and Stellar Cyber provide AI-driven case management, automated investigation capabilities, and intelligent response orchestration.
These platforms offer:
- Intelligent Case Management: AI-driven prioritization and routing of security incidents
- Multi-Agent Systems: Specialized AI agents that handle specific security tasks in parallel
- Natural Language Processing: User-friendly interfaces that allow security teams to interact with AI systems using natural language
Performance Metrics and Effectiveness
Organizations implementing AI-powered SOC solutions report significant improvements in key performance indicators:
- Mean Time to Detection (MTTD): Improved by over 8x compared to traditional SOCs
- Mean Time to Response (MTTR): Reduced by over 20x through automated incident response
- False Positive Reduction: Significant decrease in false alerts through intelligent filtering and correlation
Challenges and Limitations
Technical Challenges
Despite the significant benefits of AI-powered cybersecurity, organizations face numerous technical challenges in implementation and deployment:
Data Quality and Availability
AI systems require high-quality, representative data to function effectively. Many organizations struggle with:
- Data Fragmentation: Security data stored across multiple systems and formats
- Data Quality Issues: Inconsistent, incomplete, or biased training data
- Privacy Concerns: Challenges in sharing sensitive security data for AI training
Model Explainability and Transparency
The “black box” nature of many AI models presents challenges for security teams who need to understand how decisions are made. This is particularly important in cybersecurity, where the ability to explain and justify security decisions is crucial for incident response and forensic analysis.
Adversarial Attacks on AI Systems
AI-powered cybersecurity systems themselves become targets for sophisticated adversaries. Potential attack vectors include:
- Data Poisoning: Injection of malicious data to corrupt AI training processes
- Model Extraction: Attempts to reverse-engineer proprietary AI models
- Adversarial Examples: Carefully crafted inputs designed to fool AI detection systems
Operational Challenges
Skills Gap and Training Requirements
The implementation of AI-powered cybersecurity solutions requires specialized skills that are in short supply. Organizations must invest in:
- Staff Training: Comprehensive training programs for existing security personnel
- Talent Acquisition: Recruitment of specialists with AI and cybersecurity expertise
- Ongoing Education: Continuous learning programs to keep pace with evolving technologies
Integration with Legacy Systems
Many organizations operate complex IT environments with legacy systems that may not be compatible with modern AI-powered security solutions. This creates challenges in:
- Data Integration: Connecting AI systems with existing security infrastructure
- Workflow Adaptation: Modifying existing security processes to accommodate AI capabilities
- Performance Optimization: Ensuring AI systems don’t negatively impact existing operations
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Evolving Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory environment for AI-powered cybersecurity is rapidly evolving. Organizations must navigate:
- Data Protection Regulations: Compliance with CCPA, GDPR, , and other privacy regulations
- Industry-Specific Requirements: Sector-specific regulations such as PCI DSS for financial services
- AI Governance Frameworks: Emerging regulations specifically addressing AI system governance and accountability
Ethical Considerations
The use of AI in cybersecurity raises important ethical questions about:
- Privacy vs. Security: Balancing the need for security monitoring with individual privacy rights
- Bias and Fairness: Ensuring AI systems don’t discriminate against specific groups or individuals
- Transparency and Accountability: Maintaining clear accountability for AI-driven security decisions
Future Directions and Emerging Trends
Quantum Computing and Post-Quantum Cryptography
The advent of quantum computing poses both opportunities and threats for cybersecurity. While quantum computers could potentially break many current encryption methods, they also offer possibilities for quantum-resistant security solutions.
Key developments include:
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Development of encryption algorithms resistant to quantum attacks
- Quantum Key Distribution: Quantum-secured communication channels for sensitive data
- Hybrid Security Approaches: Combining classical and quantum security techniques
Autonomous Security Operations
The future of cybersecurity is moving toward fully autonomous security operations where AI systems can detect, investigate, and respond to threats with minimal human intervention. This evolution requires:
- Advanced AI Capabilities: More sophisticated AI models capable of complex reasoning and decision-making
- Comprehensive Automation: End-to-end automation of security processes from detection to remediation
- Human-AI Collaboration: Effective integration of human expertise with AI capabilities
Zero Trust Architecture Evolution
The Zero Trust security model continues to evolve, with AI playing an increasingly important role in:
- Continuous Authentication: Real-time verification of user identity and device integrity
- Dynamic Policy Enforcement: Automated adjustment of security policies based on risk assessment
- Behavioral Analytics: Advanced analysis of user and system behavior patterns
Implementation Strategies and Best Practices
Developing an AI Cybersecurity Strategy
Organizations seeking to implement AI-powered cybersecurity solutions should follow a structured approach:
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning
- Current State Analysis: Comprehensive assessment of existing security infrastructure and capabilities
- Risk Assessment: Identification of key security risks and vulnerabilities
- Strategic Planning: Development of a comprehensive AI cybersecurity strategy aligned with business objectives
Phase 2: Foundation Building
- Infrastructure Preparation: Establishment of necessary technical infrastructure for AI implementation
- Data Management: Implementation of data governance and management processes
- Talent Development: Training and development of internal capabilities
Phase 3: Implementation and Integration
- Pilot Programs: Small-scale implementation of AI-powered security solutions
- System Integration: Integration with existing security infrastructure
- Process Optimization: Refinement of security processes to leverage AI capabilities
Phase 4: Scaling and Optimization
- Expanded Deployment: Full-scale implementation across the organization
- Performance Monitoring: Continuous monitoring and optimization of AI systems
Best Practices for AI Cybersecurity Implementation
Governance and Risk Management
- Clear Governance Framework: Establishment of clear governance structures for AI cybersecurity initiatives
- Risk Management: Comprehensive risk assessment and mitigation strategies
- Compliance Management: Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and standards
Technology and Operations
- Hybrid Approach: Combining AI capabilities with human expertise for optimal results
- Continuous Learning: Implementation of continuous learning and improvement processes
- Performance Monitoring: Regular assessment of AI system performance and effectiveness
People and Culture
- Change Management: Comprehensive change management to address cultural and organizational impacts
- Training and Development: Ongoing training and development programs for security personnel
Economic Impact and Market Analysis
Market Growth and Investment Trends
The AI cybersecurity market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by increasing cyber threats, regulatory requirements, and technological advancements. Investment in AI cybersecurity solutions has reached record levels, with venture capital funding exceeding $290 billion over the past five years.
Regional Market Dynamics
Different regions are experiencing varying rates of AI cybersecurity adoption:
- North America: Leading in AI cybersecurity investment and implementation
- Europe: Strong regulatory focus driving AI cybersecurity adoption
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid growth in AI cybersecurity market driven by digital transformation
Industry Sector Analysis
Various industry sectors are adopting AI cybersecurity solutions at different rates:
- Financial Services: Highest adoption rate driven by regulatory requirements and high-value targets
- Healthcare: Rapid adoption driven by privacy regulations and critical infrastructure protection
- Manufacturing: Growing adoption as OT/IT convergence creates new security challenges
Return on Investment (ROI) Analysis
Organizations implementing AI-powered cybersecurity solutions report significant returns on investment:
- Cost Reduction: Average reduction in security operations costs of 15-20%
- Improved Efficiency: Significant improvements in threat detection and response times
- Risk Mitigation: Reduced impact of security incidents and data breaches
Conclusion: The Future of AI-Powered Cybersecurity
The integration of artificial intelligence into cybersecurity represents more than a technological evolution—it represents a fundamental transformation in how organizations protect themselves against cyber threats. As cyber adversaries become increasingly sophisticated and automated, the only viable defense strategy is an equally intelligent and adaptive security posture.
The evidence is clear: organizations that embrace AI-powered cybersecurity solutions are better positioned to detect, respond to, and recover from cyber threats. The market growth projections, from $22.4 billion in 2023 to a projected $134 billion by 2030, reflect the critical importance of these technologies in the modern threat landscape.
However, successful implementation requires more than just technology adoption. Organizations must develop comprehensive strategies that address technical, operational, and cultural challenges. This includes investing in talent development, establishing robust governance frameworks, and maintaining a balance between automation and human expertise.
The future of cybersecurity is not about replacing human security professionals with AI systems but about augmenting human capabilities with intelligent automation. The most successful organizations will be those that can effectively integrate AI technologies with human expertise, creating a hybrid security model that leverages the best of both approaches.
As we move forward, the question is not whether AI will transform cybersecurity, but how quickly organizations can adapt to this new reality. The window for competitive advantage is narrowing, and organizations that delay AI adoption risk being left vulnerable to increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
The convergence of AI and cybersecurity represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of digital security. Those organizations that recognize this shift early and invest strategically in AI-powered security solutions will not only protect themselves from emerging threats but will also gain significant competitive advantages in the digital economy of the future.
The future of cybersecurity is intelligent, automated, and AI-driven. The transformation is not coming—it is already here, and the time for action is now.

Supratim Sircar is an emerging thought leader in tech revolutionizing enterprise automation through agentic AI at Cisco Spaces. Currently architecting LLM-powered autonomous cloud orchestration systems as part of his M.Tech research at BITS Pilani, he transforms complex infrastructure challenges into intelligent, conversational solutions.
From building dyslexic-friendly air writing systems to automating HAProxy log analysis with conversational AI, Supratim bridges the gap between cutting-edge research and practical enterprise impact. His work spans the entire AI-cloud ecosystem—from processing 1.6M Twitter tweets on AWS Hadoop clusters to developing self-healing cloud infrastructure that understands natural language commands.
Cisco DNA Spaces TechOps STAR Excellence Award winner and Microsoft Azure Champion, Supratim doesn’t just implement AI—he reimagines how humans interact with technology, making the complex beautifully simple through code, clouds, and conversations.